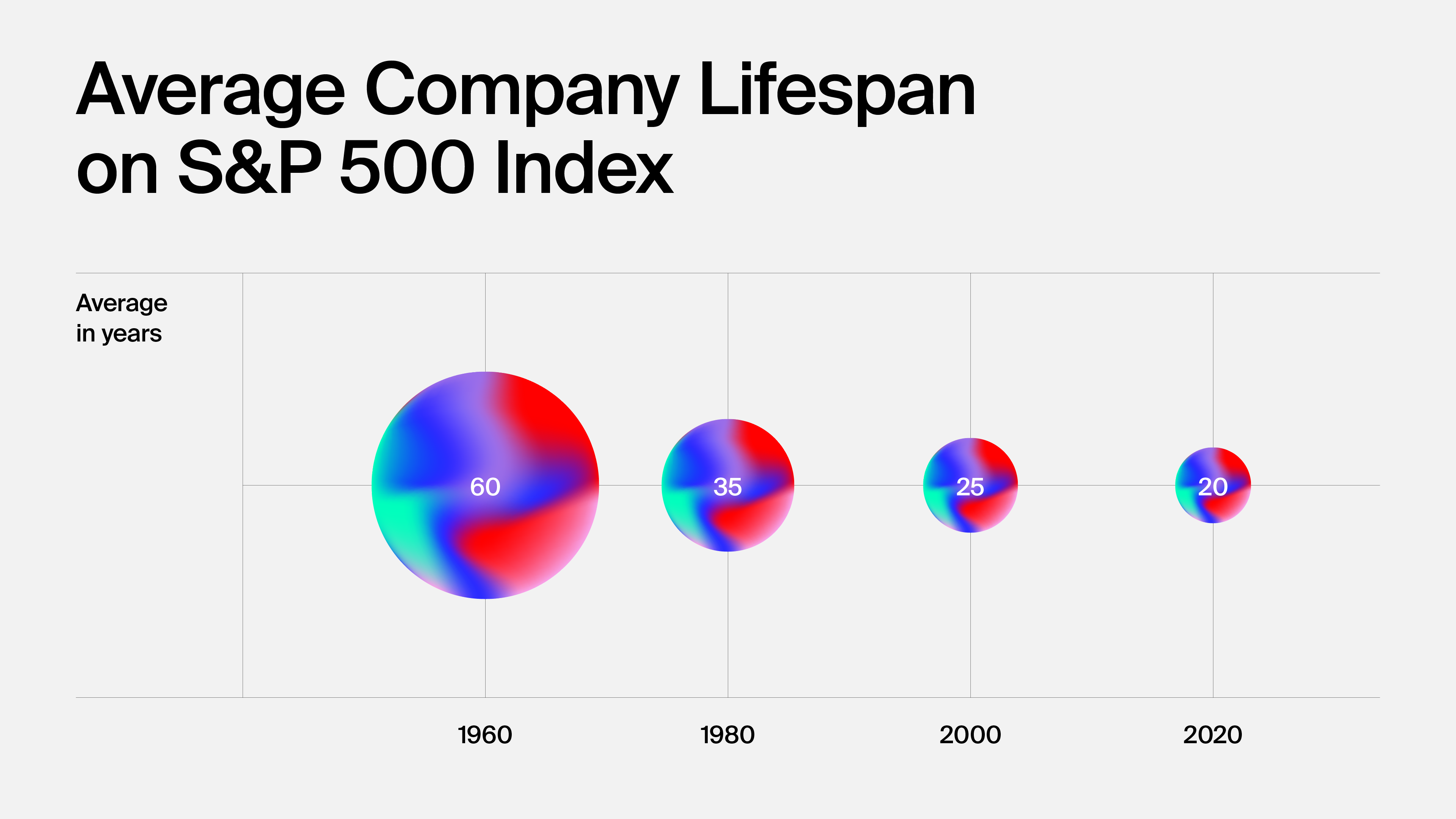
The complexity of the world we live in is increasing day by day, and so are the markets in which companies operate. Continuous innovation is necessary to keep the offering relevant and seize the many opportunities behind each change.
There are three main reasons why innovation is essential for companies:
- market volatility and fear of not satisfying a mobile and articulated demand;
- the speed of technological transformation;
- the life cycles of increasingly short business models.